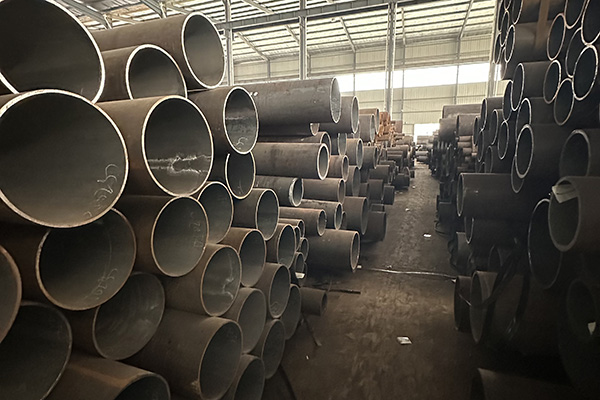
Application of Alloy Steel Pipes in High-Pressure Pipeline Systems
Alloy steel pipes play a critical role in high-pressure pipeline systems due to their superior mechanical strength, excellent thermal resistance, and enhanced corrosion resistance. These pipelines are commonly found in sectors such as oil and gas, power generation, petrochemical processing, and high-temperature steam transportation. The use of alloy steel in these systems ensures safe operation under extreme conditions, prolonged service life, and compliance with industry standards.
1. Strength and Pressure Resistance
Alloy steel pipes are designed to endure high internal pressures without deformation or failure. The addition of alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, and nickel significantly improves tensile strength and yield strength. These properties allow the pipe walls to withstand elevated pressures while maintaining dimensional stability and structural integrity.
2. Resistance to High Temperature and Thermal Cycling
In high-pressure systems, especially those involving steam or superheated fluids, operating temperatures often exceed 500°C. Alloy steel grades such as ASTM A335 P11, P22, P91, and P92 are engineered to retain their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, resisting creep deformation, thermal fatigue, and microstructural degradation.
3. Corrosion and Erosion Resistance
High-pressure pipelines frequently transport aggressive media such as sour gas, high-sulfur crude oil, or chemical-laden steam. Alloying elements like chromium and molybdenum enhance resistance to oxidation, pitting, and corrosion caused by acidic or corrosive fluids, thus reducing maintenance and improving long-term reliability.
4. Weldability and Structural Compatibility
Alloy steel pipes offer good weldability when proper preheating and post-weld heat treatment procedures are followed. This ensures strong, defect-free joints capable of withstanding high stress concentrations at weld seams. Their consistent microstructure also makes them suitable for complex pipeline networks with multiple fittings and connections.
5. Typical High-Pressure Applications
Superheater and reheater lines in power plants: Carrying high-pressure, high-temperature steam
Oil and gas transmission pipelines: Used in upstream and midstream sectors for transporting hydrocarbons under extreme pressure
Petrochemical reactor feedlines: Handling high-pressure fluids and gases in refineries and chemical plants
Boiler tubes and heat exchanger systems: In environments requiring both high thermal conductivity and pressure tolerance
Steam injection systems: For enhanced oil recovery (EOR) applications where high-pressure steam is injected into reservoirs
6. Compliance with Industry Standards
To ensure performance and safety, alloy steel pipes for high-pressure systems are manufactured according to international standards such as ASTM A335, ASTM A213, ASME B31.3, and API 5L. These standards specify mechanical properties, chemical composition, dimensional tolerances, and required testing procedures.
Conclusion
Alloy steel pipes are an indispensable component in high-pressure pipeline systems due to their high strength, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance. They provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for transporting fluids and gases under extreme pressure and temperature conditions, contributing to the safety and efficiency of critical industrial operations.
References:
ASTM A335 – Standard Specification for Seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
ASME B31.3 – Process Piping Code
API 5L – Specification for Line Pipe
ISO 3183 – Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries – Steel Pipe for Pipeline Transportation Systems
ASM Handbook, Volume 1 – Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys