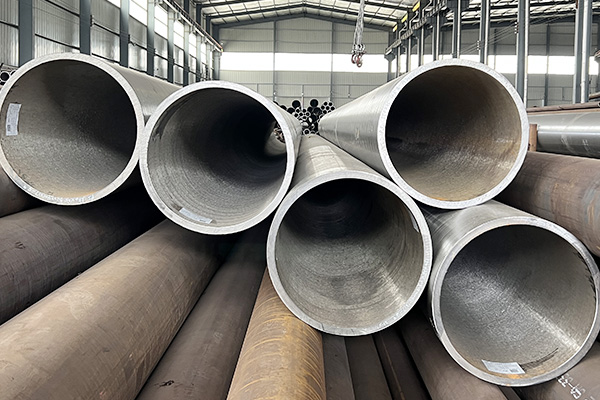
In industries that demand high reliability and durability, High Pressure Alloy Seamless Steel Pipes are critical components. Engineered to endure extreme operational pressures and temperatures, these pipes are essential for safe and efficient industrial operations. This article delves into their characteristics, material standards, and the advantages they bring to modern industrial systems.

Understanding High Pressure Alloy Seamless Steel Pipes
Unlike welded pipes, High Pressure Alloy Seamless Steel Pipes are manufactured without joints, eliminating weak points and significantly enhancing structural integrity. These pipes are particularly valuable in sectors like energy generation, chemical processing, and high-pressure boiler systems, where failure is not an option.
Key features include:
·Exceptional mechanical strength
·Resistance to elevated temperatures
·High corrosion and oxidation resistance
·Extended operational lifespan
Constructed from GR. BN materials and compliant with API 5L standards, these pipes guarantee consistent performance under demanding conditions.
Benefits of High Pressure Alloy Seamless Steel Pipes
Superior Strength and Reliability
Seamless alloy construction ensures that these pipes can withstand substantial pressure without bending or rupturing. This makes them highly suitable for high-pressure applications where operational safety is paramount.
High-Temperature Endurance
GR. BN alloys maintain mechanical integrity under extreme heat, ensuring that the pipes do not lose strength even in high-temperature environments. This property is critical in industrial processes like steam transfer or hot fluid transport.
Corrosion Protection
Industrial fluids and gases can accelerate material degradation. The alloy composition of High Pressure Alloy Seamless Steel Pipes protects against chemical corrosion, extending service life and reducing maintenance needs.
Adherence to API 5L Standards
Compliance with API 5L ensures the pipes meet stringent quality requirements, including dimensional precision and mechanical performance, making them suitable for both domestic and international projects.
Industrial Applications
These pipes are widely used across industries, including:
·Power Generation: Transporting high-pressure steam and water safely in turbines and boilers.
·Petrochemical Sector: Handling high-pressure liquids and gases with reliability.
·High-Pressure Boiler Systems: Maintaining safety and efficiency under extreme operational conditions.
The seamless design combined with premium alloy materials makes them indispensable for critical industrial systems.
Selection Guidelines
Choosing the right High Pressure Alloy Seamless Steel Pipe involves careful evaluation of:
·Pressure Tolerance: Confirm the pipe can handle the required operational pressure.
·Temperature Resistance: Ensure the GR. BN alloy maintains performance at system temperatures.
·Pipe Specifications: Verify diameter, wall thickness, and length match the system design.
·Standards Compliance: API 5L certification ensures reliable quality.
Proper selection guarantees maximum safety, efficiency, and longevity of industrial pipelines.
Maintenance Best Practices
Even high-quality seamless pipes benefit from periodic maintenance:
·Routine Inspection: Look for signs of corrosion or material wear.
·Pressure Testing: Ensure pipes maintain integrity under operational pressures.
·Cleaning Procedures: Remove deposits to maintain optimal performance and prevent corrosion.
Routine care extends service life and ensures uninterrupted operation in high-demand environments.
Conclusion
For industries operating under high pressure and temperature conditions, High Pressure Alloy Seamless Steel Pipe is a cornerstone component. Made from GR. BN alloys and conforming to API 5L standards, these pipes provide unmatched strength, reliability, and longevity. Investing in the right seamless alloy pipes ensures safety, efficiency, and dependable performance across demanding industrial applications.
References
GB/T 7714:Steel heat treatment: metallurgy and technologies[M]. CRC press, 2006.
MLA:Totten, George E., ed. Steel heat treatment: metallurgy and technologies. CRC press, 2006.
APA:Totten, G. E. (Ed.). (2006). Steel heat treatment: metallurgy and technologies. CRC press.