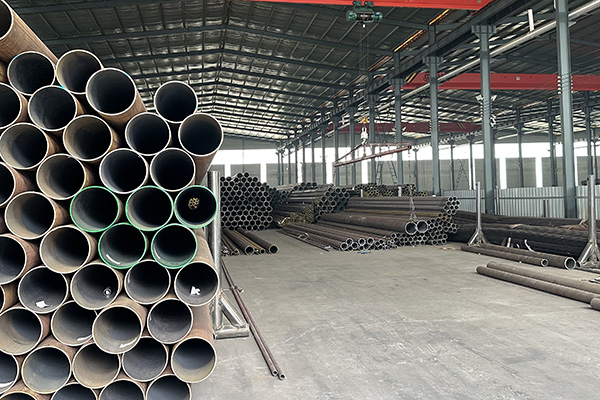
Reasons for Ellipticity Exceeding Standard of Seamless Steel Pipes
Ellipticity, also known as ovality, refers to the degree of deviation from a perfectly circular cross-section in seamless steel pipes. When the ellipticity of a pipe exceeds the standard tolerance limits specified in applicable codes (such as ASTM, EN, or API), it can lead to difficulties in installation, reduced pressure resistance, and potential safety hazards in critical applications. Several factors contribute to excessive ellipticity in seamless steel pipes:
1. Inhomogeneous Deformation During Rolling:
Uneven force distribution during hot rolling or piercing processes can result in unequal metal flow, producing an elliptical shape. Improper adjustment of the rolling mill or worn-out roller surfaces may exacerbate this problem.
2. Improper Control of Piercing Process:
In the piercing stage of manufacturing, if the centering or alignment of the billet is not accurate, or if the plug or mandrel bar is misaligned, it may lead to asymmetrical wall thinning, contributing to ellipticity.
3. Non-uniform Heating:
Inadequate or uneven heating of billets prior to rolling can cause variations in metal plasticity, leading to irregular deformation and eventual deviation from the circular form.
4. Uneven Cooling:
Post-rolling, uneven cooling on different sides of the pipe can result in stress differentials that warp the pipe into an elliptical shape.
5. Material Defects or Composition Variance:
Variations in chemical composition across the billet or inclusions within the steel can affect its flow behavior under pressure, increasing the risk of non-circularity during processing.
6. Improper Sizing or Straightening Operations:
Sizing mills are intended to calibrate the final dimensions of the pipe. If these are misaligned, worn, or poorly adjusted, they may contribute to or fail to correct elliptical deviations.
7. Inadequate Process Monitoring and Quality Control:
Lack of real-time monitoring or inadequate feedback mechanisms in the production line can allow such defects to go unnoticed until final inspection, by which time rectification may no longer be feasible.
Prevention Measures:
Calibrate and maintain rolling and piercing equipment regularly.
Ensure billets are uniformly heated before deformation.
Implement advanced non-contact measuring systems to detect ovality in-line.
Improve quality inspection of raw materials and intermediate products.
Apply controlled cooling and post-processing normalization to reduce residual stresses.
References:
Zhang, Y., & Li, M. (2018). "Causes and Control Measures of Ovality in Seamless Steel Pipe Production." Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 30(4), 66–72.
ASTM A999/A999M-20, "General Requirements for Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe."
Wu, H. (2020). "Hot Rolling Process Optimization to Reduce Ellipticity of Seamless Pipes." Materials Performance and Characterization, 9(3), 345–351.