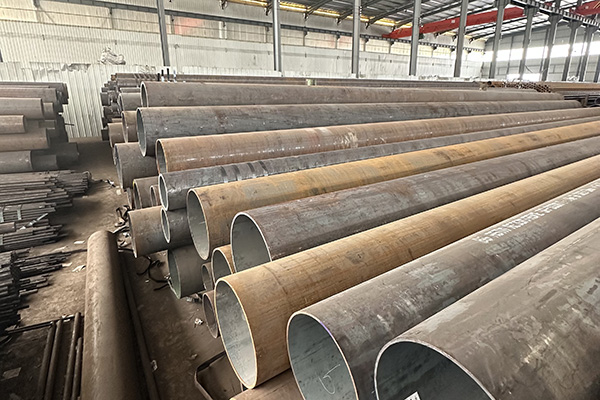
Handling Requirements for Alloy Steel Pipes during Transportation
When transporting alloy steel pipes, proper handling is essential to ensure product integrity and prevent surface damage, deformation, or contamination. Below are the key requirements and considerations for safe transportation of alloy steel pipes:
1. Packaging and Protection
Alloy steel pipes should be adequately packaged to shield them from mechanical damage and environmental exposure. Common protective measures include:
Wrapping with waterproof materials such as plastic sheeting or tarpaulin
Using wooden crates, steel frames, or pallets for support and alignment
Applying end caps to prevent damage and contamination to pipe ends
Using anti-rust coatings or oil films if pipes are prone to corrosion
2. Loading and Unloading Procedures
Handling equipment such as cranes, forklifts, or slings should be used carefully to avoid dents, scratches, or bending. The following practices are recommended:
Use soft slings or padded hooks to avoid metal-to-metal contact
Avoid dropping or dragging pipes during loading and unloading
Ensure pipes are lifted in bundles or with spreader beams to maintain balance and prevent bending
3. Stacking and Securing during Transit
Proper stacking and securing are critical to maintain stability and prevent movement:
Pipes should be stacked on flat, stable surfaces with supports between layers
Wooden or rubber spacers can be used between layers to prevent sliding and abrasion
Pipes must be securely strapped or fastened with tension belts to avoid shifting during transport
Heavier pipes should be placed at the bottom and lighter ones on top to ensure balance
4. Environmental Considerations
During long-distance transport or export, environmental protection is crucial:
Avoid direct exposure to rain or seawater, especially for pipes without anti-corrosion treatment
In maritime shipping, use containers or protective covers with desiccants to control humidity
For temperature-sensitive grades, avoid extreme temperatures that may affect material properties
5. Documentation and Identification
Each bundle or unit should be clearly labeled with:
Product specifications (e.g., grade, size, length)
Heat number and batch identification
Handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Drop,” “Keep Dry”)
This facilitates accurate delivery, inspection, and inventory control.
6. Compliance with Standards
Transportation practices should align with applicable standards such as:
ASTM A999 for general requirements of steel pipes
ISO 3183 for transportation pipeline systems
Customer-specific or contractual requirements regarding packaging and labeling
Proper handling not only protects the product but also enhances customer satisfaction, reduces claims, and upholds supply chain efficiency.
References:
ASTM A999/A999M – Standard Specification for General Requirements for Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe
ISO 3183 – Petroleum and natural gas industries — Steel pipe for pipeline transportation systems
ASME B31.3 – Process Piping Code
API 5L – Specification for Line Pipe