Installation Guidelines for High Pressure Boiler Seamless Pipe in Industrial Settings
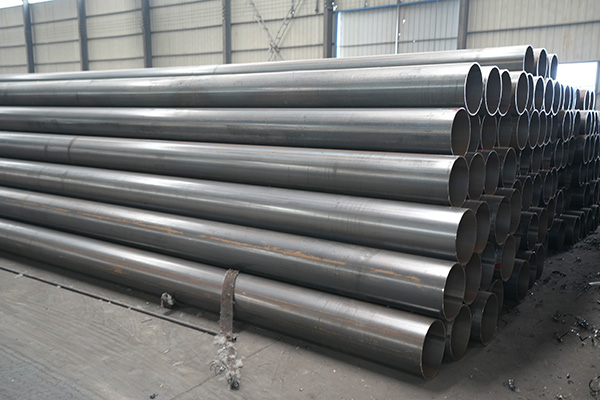
The proper installation of high pressure boiler seamless pipes is critical to ensuring safe, reliable, and long-term operation of high-pressure systems in power plants, chemical processing units, and other industrial environments. These guidelines cover key considerations before, during, and after the installation process.
1. Pre-Installation Inspection
Before installation, all seamless pipes must undergo a detailed inspection to check for surface defects, internal cracks, dimensional tolerances, and compliance with relevant standards (such as ASME SA-106 or SA-335). Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic testing and radiography are essential to verify pipe integrity.
2. Material Handling and Storage
Pipes should be handled with care to avoid mechanical damage. Use padded lifting equipment and avoid dropping or dragging the pipes. Store them in a dry, covered area to prevent corrosion, especially at the ends and edges.
3. Cleaning and Preparation
Prior to installation, pipes must be cleaned of any oil, rust, or foreign materials using suitable chemical or mechanical cleaning methods. For high-pressure boilers, internal surfaces must be smooth and free of scale to reduce turbulence and improve heat transfer efficiency.
4. Alignment and Fit-Up
Proper alignment is critical. Misalignment can lead to stress concentrations, eventual leakage, or failure. Use precision alignment tools and ensure that joint faces are square. Pipe ends should be beveled appropriately for welding, following design codes.
5. Welding and Heat Treatment
Seamless pipes for high-pressure boilers are often joined by welding. Use qualified welders and approved welding procedures in accordance with ASME Section IX. Post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) is usually required to relieve residual stresses and ensure metallurgical stability.
6. Pressure Testing
After installation and welding, the entire system should be subjected to a hydrostatic pressure test, typically 1.5 times the design pressure, to ensure there are no leaks or structural weaknesses. Pneumatic testing may be performed under specific conditions but must follow strict safety precautions.
7. Insulation and Support
Proper pipe supports must be installed to prevent sagging and thermal expansion-related stress. Use high-temperature insulation materials to conserve energy and protect personnel from hot surfaces. Ensure expansion loops or joints are included where thermal movement is expected.
8. Documentation and Compliance
Maintain complete documentation, including welding records, test reports, material certifications, and inspection checklists. Installation must comply with standards like ASME B31.1 (Power Piping) and local pressure vessel regulations.
9. Commissioning and Maintenance
After successful installation, the system should undergo commissioning procedures including flushing, leak checks, and operational verification. Scheduled maintenance is crucial to monitor performance, detect early signs of wear or corrosion, and extend service life.
References:
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section I – Power Boilers
ASME B31.1 – Power Piping Code
ASTM A106/A106M – Standard Specification for Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
ASTM A335/A335M – Standard Specification for Seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
API RP 574 – Inspection Practices for Piping System Components